Mail Transfer Agent-Strict Transport Security (MTA-STS) is a new standard that enables mail service providers with the ability to enforce Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure SMTP connections, and to specify whether the sending SMTP servers should refuse to deliver emails to MX hosts that that does not offer TLS with a reliable server certificate. It has been proven to successfully mitigate TLS downgrade attacks and Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks.
In simpler terms, MTA-STS is an internet standard that secures connections between SMTP mail servers. The most prominent problem with SMTP is that encryption is completely optional and isn’t enforced during mail transfer. This is why SMTP adopted the STARTTLS command to upgrade from plaintext to encryption. This was a valuable step towards mitigating passive attacks, however, tackling attacks via active networks and MITM attacks still remained unaddressed.
Hence, the issue MTA-STS is solving is that SMTP utilizes opportunistic encryption, i.e if an encrypted communication channel cannot be established, the connection falls back to plaintext, thereby keeping MITM and downgrade attacks at bay.
What is a TLS Downgrade Attack?
As we already know, SMTP did not come with an encryption protocol and encryption had to be retrofitted later on to enhance the security of the existing protocol by adding the STARTTLS command. If the client supports encryption (TLS), it will understand the STARTTLS verb and will initiate a TLS exchange before sending the email to ensure it is encrypted. If the client doesn’t know TLS, it will simply ignore the STARTTLS command and send the email in plaintext.
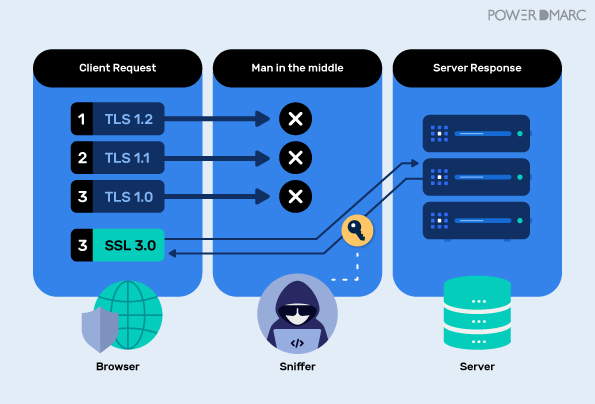
Therefore, since encryption had to be retrofitted into SMTP protocol, the upgrade for encrypted delivery has to rely on a STARTTLS command that is sent in cleartext. A MITM attacker can easily exploit this feature by performing a downgrade attack on the SMTP connection by tampering with the upgrade command. The attacker simply replaced the STARTTLS with a garbage string which the client fails to identify. Therefore, the client readily falls back to sending the email in plaintext.
The attacker usually replaces the command with the garbage string containing the same number of characters, rather than chucking it out, because this preserves the packet size and therefore, makes it easier. The eight letters in the garbage string in the option command allow us to detect and identify that a TLS downgrade attack has been executed by a cybercriminal, and we can measure its prevalence.
In short, A downgrade attack is often launched as a part of a MITM attack, so as to create a pathway for enabling a cryptographic attack that would not be possible in case of a connection that is encrypted over the latest version of TLS protocol, by replacing or deleting the STARTTLS command and rolling back the communication to cleartext.
While it is possible to enforce TLS for client-to-server communications, as for those connections we know that the apps and the server support it. However, for server-to-server communications, we must fail open to allow legacy servers to send emails. The crux of the problem is that we have no idea if the server on the other side supports TLS or not. MTA-STS allows servers to indicate that they support TLS, which will allow them to fail close (i.e. not sending the email) if the upgrade negotiation doesn’t take place, thereby making it impossible for a TLS downgrade attack to take place.

How Does MTA-STS Come to the Rescue?
MTA-STS functions by increasing the EXO or Exchange Online email security and is the ultimate solution to a wide range of SMTP security drawbacks and problems. It solves issues in SMTP security such as lack of support for secure protocols, expired TLS certificates, and certificates that are not issued by reliable third parties.
As mail servers proceed to send out emails, the SMTP connection is vulnerable to cryptographic attacks such as downgrade attacks and MITM. Downgrade attacks can be launched by deleting the STARTTLS response, thereby delivering the message in clear text. Similarly, MITM attacks can also be launched by redirecting the message to a server intruder over an insecure connection. MTA-STS allows your domain to publish a policy that makes sending an email with encrypted TLS compulsory. If for some reason the receiving server is found to not support STARTTLS, the email will not be sent at all. This makes it impossible to instigate a TLS downgrade attack.
In recent times, the majority of mail service providers have adopted MTA-STS thereby making connections between servers more secure and encrypted over TLS protocol of an updated version, thereby successfully mitigating TLS downgrade attacks and nullifying the loopholes in server communication.
PowerDMARC brings to you, speedy and easy hosted MTA-STS services which make your life a whole lot easier as we take care of all the specifications required by MTA-STS during and after implementation, such as an HTTPS-enabled web server with a valid certificate, DNS records, and constant maintenance. PowerDMARC manages all of that completely in the background so that after we help you set it up, you never even have to think about it again!
With the help of PowerDMARC, you can deploy Hosted MTA-STS at your organization without the hassle and at a very speedy pace, with the help of which you can enforce emails to be sent to your domain over a TLS encrypted connection, thereby making your connection secure and keeping TLS downgrade attacks at bay.
- The Rise of Pretexting Scams in Enhanced Phishing Attacks - January 15, 2025
- DMARC for PCI DSS 4.0 Compliance – Mandatory from 2025 - January 12, 2025
- NCSC Mail Check Changes & Their Impact on UK Public Sector Email Security - January 11, 2025